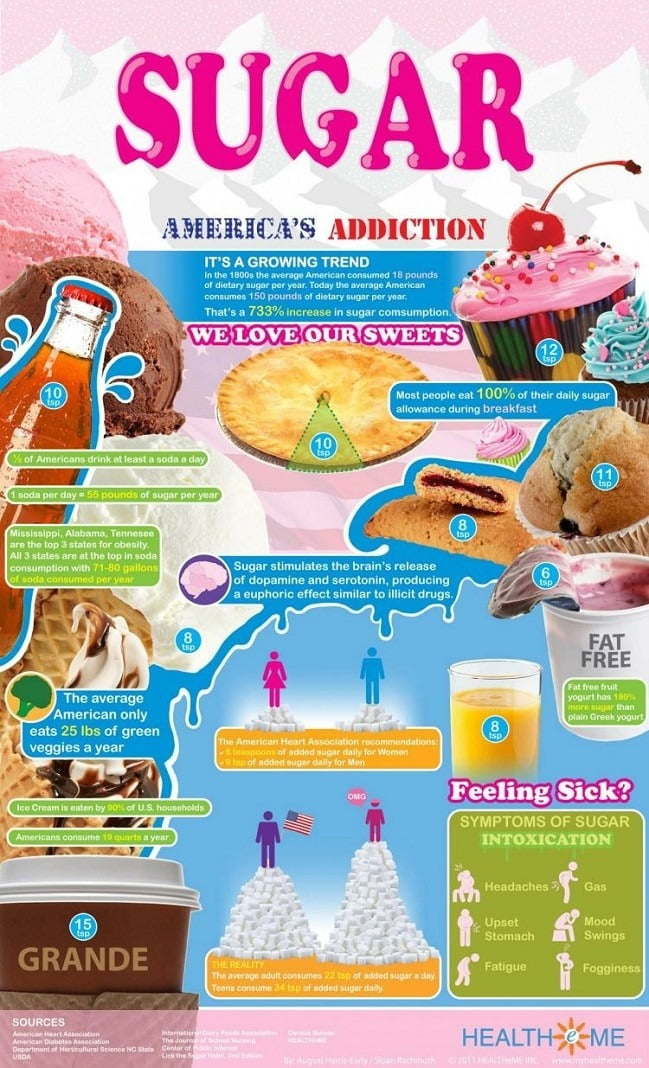
Sugar addiction is a growing concern in today’s society, as many individuals grapple with the effects of sugar on their health and cravings. Research suggests that while sugar is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, it does lead to significant sugar cravings and compulsive eating behaviors. The health risks of sugar consumption, especially from ultra-processed foods, have become increasingly evident, prompting many to wonder, “Is sugar addictive?” These food items not only contain high levels of added sugars but also unhealthy fats and sodium that can intensify cravings and habitual consumption. Understanding the psychological and physical effects of sugar is crucial for managing intake and promoting healthier lifestyle choices.
The concept of sugar dependency often overlaps with terms like sweet tooth or sugar cravings, reflecting an intricate relationship many have with this common ingredient. While not entirely synonymous with substance dependency, the habitual consumption of sugary products can lead to adverse health implications, making it essential to explore the overall effects associated with excessive sugar intake. For many, the allure of sweet treats can result in a cycle of mild withdrawal symptoms when intake is reduced, indicating the complexities involved in moderating sugar consumption. Recognizing the potential health risks of sugars from both a nutritional and psychological perspective can provide insights into why many find it difficult to resist sugary delights, even when aware of these dangers.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
Sugar addiction is a complex issue that often ignites fierce debates among nutrition experts. While the majority agree that sugar can stimulate cravings similar to those caused by addictive drugs, its classification remains ambiguous. The root of the problem lies in the way sugar affects our brain’s reward system. Consuming high-sugar foods releases dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward, which can lead to compulsive eating behaviors. This reaction can set the stage for people to crave sugar intensely, much like other substances known for their addictive qualities.
However, it is essential to recognize that, unlike substances such as nicotine and alcohol, sugar is not classified as addictive in clinical terms. According to nutrition researcher Frank Hu, while reducing sugar intake can result in withdrawal-like symptoms, these effects are generally less severe than those experienced with true addictive substances. The abundance of processed foods loaded with added sugars exacerbates the situation as they make it easier to consume sugar in large amounts, contributing to cravings and potentially leading to health risks such as obesity, heart disease, and diabetes.
Effects of Sugar on Your Health
The health effects of sugar consumption are a significant concern, especially given the average American’s intake of nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar per day. High sugar consumption can lead to various health problems, including weight gain and increased risk of chronic diseases. Sugar has been linked to cardiovascular issues, as excessive consumption can lead to inflammation and insulin resistance, both of which are precursors to heart disease. Additionally, high sugar diets can contribute to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, highlighting the myriad health risks associated with sugar.
Moreover, the effects of sugar extend beyond physical health. High sugar intake can negatively impact mental health as well. Studies suggest that diets high in sugar can increase the risk of developing depression and anxiety. These psychological implications stem from the fluctuations in blood sugar levels, which can lead to feelings of irritability or a ‘sugar crash’. As such, moderating sugar consumption not only benefits physical well-being but also enhances mental clarity and emotional stability.
Why Do We Experience Sugar Cravings?
Sugar cravings can be perplexing, yet they are rooted in both biological and psychological factors. When we consume sugar, our brain releases feel-good chemicals like dopamine, creating a pleasurable experience that can lead to cravings for more. Additionally, our environment plays a crucial role; the omnipresence of sweet treats in modern society can condition us to crave sugar, often leading to habitual consumption. This cycle can be challenging to break, as the immediate reward of sugar intake reinforces the desire for sweets.
Moreover, factors such as stress, lack of sleep, and poor nutrition can amplify sugar cravings. When we are stressed, our body tends to crave quick energy sources, and sugar provides that instant satisfaction. Nutritional deficiencies can also impact how our body processes energy, causing us to seek out sugary foods as a source of comfort. Understanding the triggers behind sugar cravings can help individuals develop healthier eating habits, ultimately leading to a more balanced approach to nutrition.
The Role of Processed Foods in Sugar Consumption
Processed foods are a significant contributor to the high levels of sugar consumption in many diets today. These foods often contain added sugars that enhance flavor and shelf life, making them appealing and addictive for consumers. Items like sugary beverages, snacks, and desserts contribute to the increasing prevalence of sugar addiction-like behaviors. The convenience and palatability of these foods make it easy to overconsume, often leading individuals to exceed their recommended daily sugar intake without even realizing it.
Additionally, the marketing of processed foods often targets children and adolescents, further embedding sugar consumption in daily life. As these young consumers develop preferences for sweet flavors, they are more likely to gravitate toward sugary products throughout their lives. Raising awareness about the detrimental effects of processed foods on sugar consumption is vital in promoting healthier dietary choices and reducing the associated health risks such as obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Strategies to Manage Sugar Intake
Managing sugar intake is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. One effective strategy is to gradually reduce the amount of added sugar in your diet rather than eliminating it entirely. Going cold turkey can lead to intense cravings and potential binge eating. Instead, start by replacing sugary snacks and drinks with healthier alternatives like fruit or yogurt. Reading food labels can also provide valuable insights into hidden sugars in packaged foods, empowering individuals to make better choices.
Additionally, balancing meals with protein, fiber, and healthy fats can help stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce cravings. When meals are well-rounded, there is a lower likelihood of experiencing energy crashes that often lead to sugar cravings. Staying hydrated and getting adequate sleep are also essential components of sugar management, as both factors can influence how we perceive hunger and cravings. By implementing these strategies, individuals can cultivate a healthier relationship with sugar and improve their overall health.
The Psychological Perspective on Sugar
From a psychological standpoint, understanding our relationship with sugar is essential. Many people use sugary foods as a form of emotional comfort, turning to sweets in times of stress, sadness, or even boredom. This emotional eating can become a coping mechanism, leading to habitual sugar consumption, which may not only cause weight gain but also contribute to feelings of guilt or shame. Acknowledging these emotional triggers is the first step in overcoming the psychological barriers related to sugar addiction.
Cognitive-behavioral approaches can be effective in reprogramming how we think about and interact with sugar. Techniques such as mindful eating encourage individuals to become more aware of their cravings and the emotions tied to their sugar consumption. This awareness can help break the cycle of emotional eating and promote healthier choices. By addressing the psychological aspects of sugar cravings, individuals are more likely to develop balanced eating habits that do not rely on sugary comfort foods.
Health Risks Associated with Excess Sugar Consumption
Excessive sugar consumption poses significant health risks that are increasingly concerning in our modern diet. Leading health organizations, like the American Heart Association, emphasize the importance of limiting added sugar intake to reduce the risks of chronic health conditions. The link between high sugar consumption and obesity is profound, with sugar-sweetened beverages being particularly problematic. Regularly consuming these drinks can lead to weight gain and an increased risk of metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes.
Moreover, sugar is not just a contributor to obesity but also plays a role in heart disease. High intake of added sugars can lead to increased triglycerides and blood pressure, both of which are key risk factors for cardiovascular disease. As the evidence mounts regarding the health risks associated with sugar, it becomes even clearer that moderating sugar intake is essential for long-term health and wellness.
Finding Balance: Can We Have Sugar in Moderation?
The question of whether we can include sugar in our diets without facing health consequences often arises. The key is moderation. It is entirely possible to enjoy sweet treats while maintaining a balanced diet, provided that sugar intake is kept within recommended limits. Incorporating natural sources of sugar, such as fruits, can offer both taste and nutritional benefits without the adverse effects associated with added sugars. By embracing moderation, individuals can satisfy their sweet cravings without compromising their overall health.
Additionally, finding balance includes being mindful of the types of sugars consumed. While natural sugars found in whole foods are accompanied by essential nutrients and fiber, added sugars in processed foods provide empty calories without nutritional benefits. Hence, choosing whole, unprocessed foods over sugary snacks can support a healthier approach. By cultivating a mindset that allows for indulgence in moderation, individuals can create a sustainable relationship with sugar and enjoy the sweetness in life.
The Future of Sugar Consumption in Our Diets
As awareness of the health risks associated with sugar grows, the future of sugar consumption in our diets is likely to shift significantly. Public health initiatives aimed at reducing sugar intake emphasize the need for policy changes, such as implementing taxes on sugary beverages and mandating clear labeling on food products. These measures can help educate consumers and encourage them to make informed food choices that prioritize health over convenience.
In addition, emerging trends show a growing demand for healthier alternatives to sugar. As consumers become more health-conscious, the market for natural sweeteners and sugar substitutes is expanding. Innovations in food technology may lead to the development of better tasting and healthier options that can fulfill our sweet cravings without the downsides of traditional added sugars. The key to future sugar consumption will lie in a collective effort to prioritize health, balance, and informed choices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like alcohol or nicotine?
While sugar can increase cravings and lead to compulsive eating behaviors, it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. The debate around sugar addiction exists because consuming ultra-processed foods high in added sugar can create withdrawal-like symptoms, but these effects vary in intensity compared to substances that are strictly addictive.
What are the effects of sugar on the brain?
Sugar consumption can impact the brain by triggering the release of pleasure-inducing chemicals such as dopamine. This can create a pattern of cravings and habitual eating, making sugar consumption feel rewarding. However, the psychological effects may not be as intense as those related to addictive drugs, suggesting a complex relationship with sugar.
How do sugar cravings occur?
Sugar cravings can occur due to the body’s response to consuming high amounts of added sugars, particularly from sweetened beverages and snacks. Such cravings can be triggered by the brain’s reward system, which associates sugar with pleasure and satisfaction. Reducing sugar intake gradually can help manage and reduce these cravings over time.
What are the health risks of high sugar consumption?
High sugar consumption is associated with numerous health risks, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and dental problems. The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar to no more than 9 teaspoons for men and 6 for women to mitigate these risks and promote better health.
How can I reduce my sugar intake effectively?
To effectively reduce sugar intake, start by reading food labels to become aware of added sugars in processed foods. Gradually decrease sugar consumption rather than quitting cold turkey, as this approach can prevent withdrawal symptoms and promote long-term success. Incorporating whole foods and maintaining a balanced diet can also help manage cravings.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Sugar Addiction Debate | Sugar is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, but it can lead to cravings and compulsive eating. |
| Food System Impact | Ultra-processed foods high in added sugars can heighten cravings and promote habitual consumption, which can result in withdrawal-like symptoms. |
| Moderate Sugar Consumption | Low to moderate amounts of sugar can be part of a balanced diet without major health consequences. |
| Recommended Sugar Intake | AHA suggests no more than 9 teaspoons for men, 6 teaspoons for women, and lower for children. |
| Gradual Reduction | It’s better to gradually reduce sugar intake rather than abruptly cutting it out. |
Summary
Sugar addiction is a complex topic that stirs much debate among health researchers. While sugar is often likened to addictive substances like nicotine and alcohol due to its ability to create cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, it lacks the clinical classification as an addictive drug. Understanding sugar’s role in our diet is crucial; moderate consumption can enhance flavors and texture without adverse health effects. Recognizing the distinction between necessary nutrients and addictive substances can help individuals effectively manage their sugar intake and lead a healthier lifestyle.