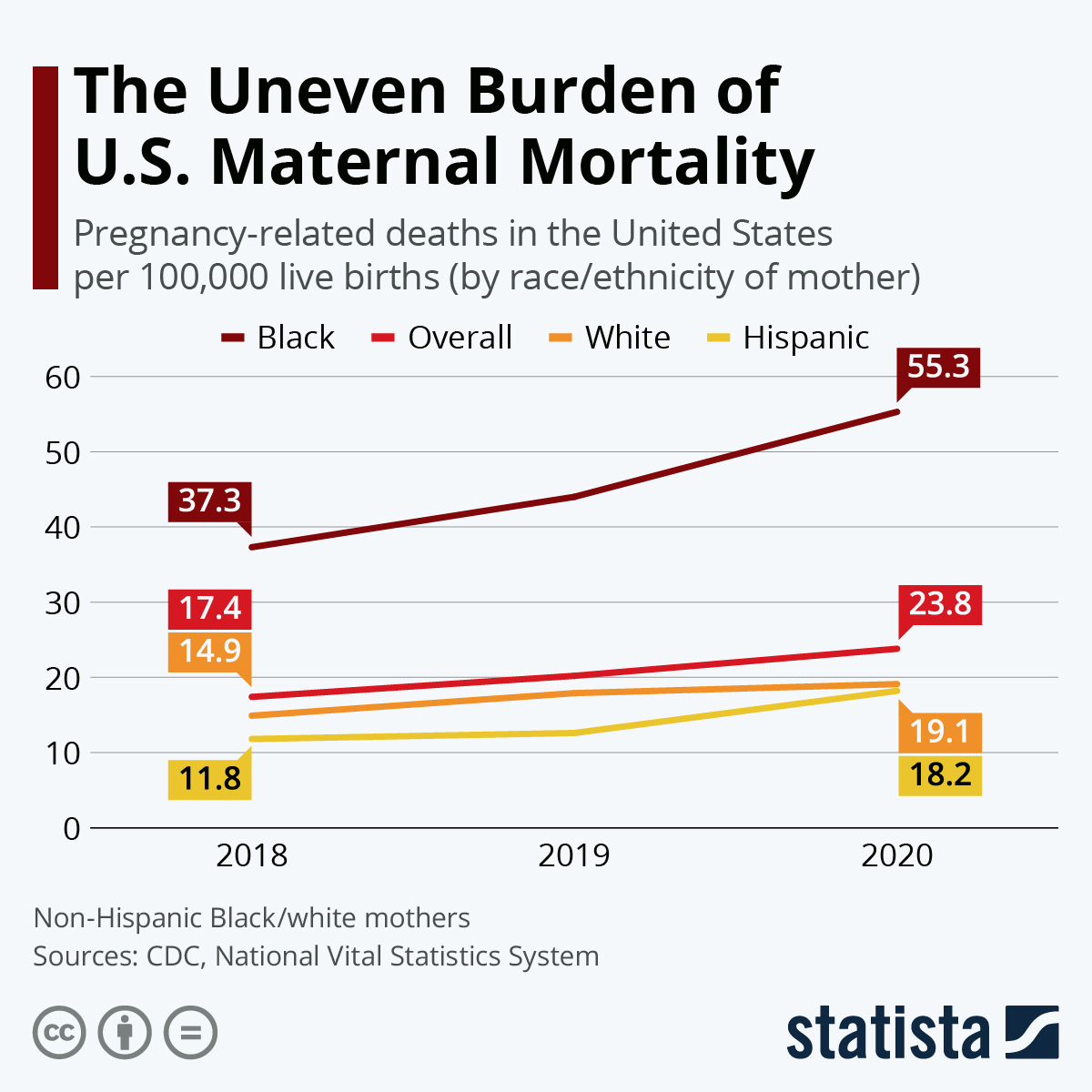
Maternal mortality in the U.S. remains an alarming public health crisis, as recent studies reveal an upward trend in pregnancy-related deaths among American women. Despite the fact that over 80% of these deaths are preventable, the United States leads high-income nations in maternal mortality rates, underscoring critical gaps in maternal health services. From 2018 to 2022, disparities in outcomes proliferated across various demographics, with significant variations observed by state and racial background. Enhanced prenatal care and comprehensive postpartum care are essential factors in combatting this issue, yet many women experience inadequate healthcare support throughout their pregnancy journeys. Addressing health disparities and ensuring equitable access to quality maternal health resources is vital to reversing this alarming trend.
The growing incidence of pregnancy-related fatalities in the United States brings to light a pressing health dilemma that calls for urgent intervention. These maternal health complications, particularly among marginalized groups, highlight the urgent need for improved prenatal and postpartum healthcare systems. Despite advancements in medical technologies, the persistent challenges of access and systemic bias continue to contribute to preventable deaths during and after pregnancy. The broad spectrum of maternal health issues, including inadequate prenatal care and insufficient postpartum support, indicates an urgent need for policy reforms aimed at safeguarding the lives of mothers. As maternal health outcomes increasingly reflect disparities influenced by socioeconomic factors, it becomes imperative to prioritize this critical issue to ensure the safety and well-being of all pregnant individuals.
Understanding Maternal Mortality in the U.S.
Maternal mortality in the U.S. has reached alarmingly high levels, particularly when compared to other high-income countries. A recent study revealed that the U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among its peers, with more than 80 percent of these deaths being preventable. This startling statistic exposes the inefficiencies within the healthcare system and highlights the urgency for comprehensive reforms in maternal health policies. Understanding the factors contributing to these deaths is critical, as it offers pathways to improve prenatal and postpartum care, reducing the risk of pregnancy-related fatalities.
The rising rates of maternal mortality can largely be attributed to a fragmented healthcare system and significant health disparities experienced across different racial and ethnic groups. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women face a mortality rate nearly four times that of white women. These disparities underscore the need for targeted interventions, particularly in areas that lack access to quality prenatal care. Addressing these issues through holistic approaches that involve community outreach and education may significantly reduce the risks associated with pregnancy and childbirth.
The Role of Prenatal Care in Reducing Pregnancy-Related Deaths
Access to quality prenatal care is essential in mitigating the risks associated with pregnancy-related deaths. Comprehensive prenatal services help monitor and manage potential health issues, such as hypertension and diabetes, which can complicate pregnancy. By ensuring that expectant mothers receive regular check-ups and necessary screenings, healthcare providers can identify and address problems before they escalate. Increasing awareness about the importance of prenatal care can empower women to seek timely medical attention, ultimately improving maternal health outcomes.
Moreover, the integration of educational programs focusing on the benefits of prenatal care can foster a culture of preventative health among pregnant individuals. These programs should emphasize the significance of attending all prenatal appointments and adhering to medical advice. Additionally, there should be increased efforts to provide accessible prenatal services in maternity care deserts, where gaps in healthcare resources are prevalent. Efforts to improve transportation options and offer telehealth services may also enhance access to prenatal care, ensuring that all women receive the support they need throughout their pregnancy.
Postpartum Care: A Critical Component of Maternal Health
Postpartum care is a crucial yet often overlooked aspect of maternal health. The World Health Organization recognizes only deaths occurring up to 42 days after childbirth as maternal mortality; however, recent studies indicate that nearly a third of pregnancy-related deaths occur within the first year postpartum. This highlights the necessity for healthcare systems to extend support and resources beyond the traditional six-week postpartum checkup, ensuring women receive adequate care as they navigate their recovery.
Expanding postpartum care to include mental health services, chronic disease management, and ongoing health education can significantly reduce the rates of late maternal deaths. Women face numerous challenges in the months following childbirth, including mental health struggles, physical health complications, and social support deficits. By fostering a continuum of care that addresses these issues holistically, healthcare providers can improve maternal health outcomes and better align with the needs of new mothers.
Health Disparities and Maternal Outcomes
Health disparities play a significant role in maternal mortality rates in the U.S. Systemic inequities in healthcare access, racial biases, and socioeconomic factors contribute to significantly varying outcomes for women during pregnancy. Research shows that American Indian and Alaska Native women and non-Hispanic Black women experience disproportionately higher rates of pregnancy-related deaths. These disparities demand immediate attention and targeted policy interventions to ensure that all women, regardless of their background, have access to quality maternal care.
Addressing health disparities in maternal health requires a multi-faceted approach that includes improving healthcare access, promoting cultural competency among providers, and investing in community-driven health initiatives. For example, incorporating traditional practices and beliefs into maternal care can enhance trust and engagement among marginalized groups. By prioritizing equity in maternal care, we can work towards eliminating the racial and ethnic disparities that lead to unnecessary loss of life.
Innovative Solutions to Combat Maternal Mortality
To reduce maternal mortality in the U.S., innovative solutions must be employed to revamp the current healthcare system. State-level policies should promote the integration of interdisciplinary care models that address the varied and complex needs of pregnant individuals. For instance, implementing home visits and community health worker programs can enhance access to care for marginalized populations, ultimately reducing the risk of pregnancy-related deaths.
Additionally, healthcare systems should invest in training programs that elevate the quality of communication and cultural sensitivity among providers. Ensuring that healthcare professionals understand the unique challenges faced by different demographics can improve patient-provider relationships and encourage women to seek help when needed. By prioritizing innovation and collaboration in maternal healthcare, we can begin to see meaningful changes in the rates of pregnancy-related deaths.
The Impact of Chronic Conditions on Maternal Health
Chronic conditions such as hypertension and cardiovascular disease are increasingly prevalent among women of reproductive age in the U.S. This shift poses a significant risk during pregnancy, as these conditions can lead to severe complications and increase the likelihood of maternal mortality. Studies indicate that more young women in their 20s and 30s are being diagnosed with chronic diseases compared to previous decades, highlighting an urgent need for targeted interventions to manage these health issues before, during, and after pregnancy.
Preventative strategies focusing on maintaining cardiovascular health and managing chronic conditions are essential in reducing pregnancy-related deaths. Access to pre-conception care that includes screenings for chronic health issues can help women better prepare for pregnancies and mitigate the associated risks. Efforts to educate women on lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise, can also support overall well-being and reduce the chances of complications during pregnancy.
Empowering Women Through Education and Advocacy
Education and advocacy play a crucial role in redefining maternal health outcomes in the U.S. Empowering women with knowledge about their reproductive health, rights, and available resources can lead to more informed decision-making during pregnancy. Community-based educational initiatives can raise awareness about prenatal and postpartum care, helping expectant and new mothers understand the importance of seeking help when needed.
Advocating for systemic change in maternal healthcare policies is equally crucial. Implementing programs that involve women as active participants in their care can create a more supportive environment for maternal health. By raising awareness, addressing biases, and promoting policies that ensure access to quality care, we can combat the rising rates of maternal mortality and strengthen the health outcomes for future generations of mothers.
The Role of Public Health Infrastructure in Maternal Mortality Prevention
A robust public health infrastructure is vital in addressing the ongoing crisis of maternal mortality in the U.S. Investment in data collection, tracking pregnancy-related deaths, and analyzing demographics will improve our understanding of the maternal health landscape. Strengthening public health systems enables quicker responses to emerging trends and potential crises, ensuring that resources are allocated effectively to support mothers at risk.
Moreover, the integration of maternal health services within community health frameworks can facilitate better outcome tracking and intervention strategies. Public health initiatives should focus on improving maternal care access in underserved communities, implementing preventive strategies, and advocating for long-term investments in maternal health. By fortifying public health infrastructure, we can enhance overall maternal health outcomes and significantly impact reducing mortality rates.
Advancing Maternal Health Research for Improved Outcomes
Advancing research in maternal health is essential to tackling the complexities surrounding pregnancy-related deaths. Enhanced funding for research initiatives focused on maternal mortality will allow for a deeper understanding of the contributing factors, particularly regarding race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status. Collaborating with academia, government agencies, and public health organizations can yield valuable insights, fostering an evidence-based approach to addressing maternal health disparities.
Engaging with communities affected by maternal mortality can also guide research efforts. Grassroots involvement allows researchers to tailor studies to address localized needs and concerns, making them more relevant and actionable. By prioritizing maternal health research and aligning it with community needs, we can develop effective interventions and policies that significantly reduce maternal mortality rates and promote better outcomes for all mothers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary causes of maternal mortality in the U.S.?
In the U.S., the primary causes of maternal mortality include cardiovascular disease, hemorrhage, and infection. Recent studies show that cardiovascular disease has become the leading cause, accounting for over 20% of pregnancy-related deaths. This shift reflects rising rates of chronic conditions such as hypertension among pregnant individuals.
How can prenatal care impact maternal mortality in the U.S.?
Effective prenatal care is crucial in reducing maternal mortality in the U.S. By identifying and managing health conditions early in pregnancy, consistent prenatal visits can help prevent complications that lead to pregnancy-related deaths. Unfortunately, disparities in access to quality prenatal care continue to exist across different states and racial groups.
What role does postpartum care play in preventing maternal mortality?
Postpartum care is essential for monitoring the health of new mothers and addressing potential issues that can arise after childbirth. In the U.S., nearly a third of maternal mortality cases occur after the initial postpartum period, indicating the need for ongoing healthcare support beyond the traditional six-week check-up.
Why is maternal mortality rising in the United States compared to other high-income countries?
The rise in maternal mortality in the U.S. compared to other high-income countries can be attributed to a fragmented healthcare system, unequal access to services, and persistent racial and ethnic healthcare disparities. Factors like chronic health conditions also contribute to higher pregnancy-related death rates in certain demographics.
What are the health disparities affecting maternal mortality rates in the U.S.?
Health disparities significantly affect maternal mortality rates in the U.S., with American Indian and Alaska Native women facing the highest rates of pregnancy-related deaths. Additionally, non-Hispanic Black women also experience mortality rates significantly higher than white women, underscoring the impact of systemic inequities in maternal health care.
How does the COVID-19 pandemic affect maternal mortality in the United States?
The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated maternal mortality rates in the United States, particularly in 2021. Many women faced barriers to care, increased stress, and health complications from COVID-19, contributing to a rise in pregnancy-related deaths during this period. The pandemic highlighted the urgent need for improved maternal health systems.
What are ‘late maternal deaths’ and why are they significant in maternal health?
‘Late maternal deaths’ refer to deaths occurring between 42 days and one year postpartum. These deaths account for nearly a third of maternity-related fatalities in the U.S., highlighting the importance of extending maternal health care and support into the postpartum period, which is often neglected in standard health discussions.
What measures can be taken to reduce maternal mortality in the U.S.?
To reduce maternal mortality in the U.S., it is vital to invest in public health infrastructure, enhance the quality of prenatal and postpartum care, address health disparities, and implement policies that support equitable healthcare access. Fostering health education and awareness about maternal health can also play a key role.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Maternal Mortality in the U.S. | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, continuing to rise, with 80% of these deaths being preventable. |
| Racial Disparities | Significant disparities exist in maternal mortality: American Indian and Alaska Native women have the highest rates, followed by non-Hispanic Black and white women. |
| Leading Causes of Death | Cardiovascular disease accounts for over 20% of pregnancy-related deaths, a shift from hemorrhage as the leading cause. |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Late maternal deaths (42 days to 1 year postpartum) make up nearly a third of total deaths, highlighting the need for extended postpartum care. |
| Need for Improved Care | Investment in public health infrastructure and innovative solutions for quality care during pregnancy and extended postpartum is crucial. |
| COVID-19 Impact | The pandemic appears to have exacerbated rising rates, particularly in 2021, but the upward trend was evident before even the pandemic began. |
Summary
Maternal mortality in the U.S. has reached alarming levels, emphasizing the urgent need for systemic changes in healthcare delivery and access to care for expecting mothers. With more than 80% of these tragedies considered preventable, the focus must shift towards addressing disparities, particularly those affecting racial and ethnic minorities. Significant policy adjustments, coupled with increased investment in public health infrastructure, are essential to combat the worrying rise in pregnancy-related deaths and to ensure healthier outcomes for mothers across the nation.